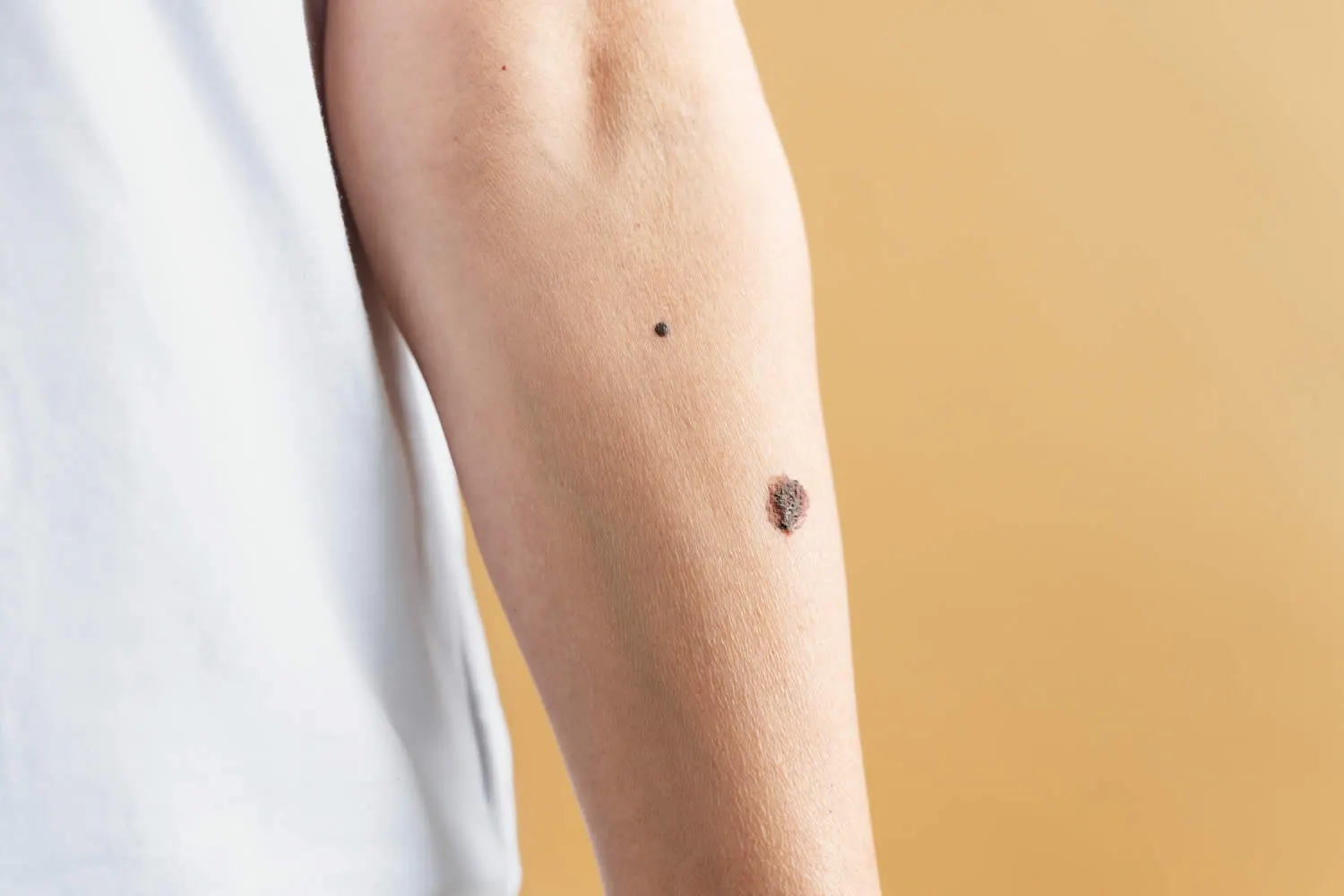
What are Moles?
A mole is a type of skin lesion that is caused by the growth of pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. Moles can appear anywhere on the skin and can be various shapes, sizes, and colors, including black, brown, or flesh-colored. Some moles are present at birth, while others may develop over time. Most moles are benign, but in rare cases, moles can develop into skin cancer, so it’s important to monitor any changes in their appearance and have any suspicious moles evaluated by a dermatologist or skin care professional.
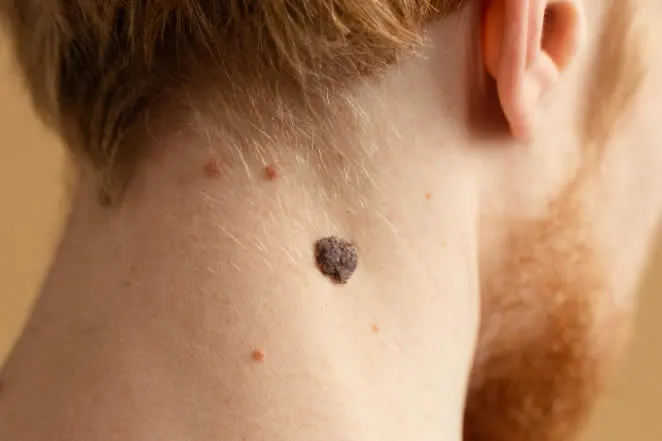
What are the causes of Moles?
Moles are caused by the overgrowth of pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. The exact reason for this overgrowth is not fully understood, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play a role, including:
- Genetics: The tendency to develop moles can be inherited.
- Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV rays from the sun can increase the risk of developing moles.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or puberty, can cause the growth of new moles or changes in existing moles.
- Age: Moles are more common in younger people and tend to fade or disappear as people age.
- Skin type: People with fair skin and lighter hair are more susceptible to developing moles.
It’s also worth noting that some moles can develop as a result of injury or irritation to the skin, such as from friction or rubbing.
What treatments are available for Moles at the dermatologist in St. Louis?
The treatment for moles depends on various factors, such as the type, size, and location of the mole, as well as any changes in its appearance. Some common treatments include:
- Observation: If a mole is benign and not causing any symptoms, a dermatologist may recommend monitoring it for any changes over time.
- Surgical removal: Moles can be surgically removed by a dermatologist or skin care professional, either by cutting them out (excision), shaving them off (curettage), or using a laser.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves freezing the mole with liquid nitrogen, which causes the mole tissue to blister and eventually fall off.
- Topical medications: In some cases, topical medications, such as imiquimod, may be used to treat moles by encouraging the immune system to attack the mole cells.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy uses light energy to destroy the mole cells without damaging the surrounding skin.
It’s important to note that any changes in a mole’s appearance, such as itching, bleeding, or changes in color, shape, or size, should be evaluated by a dermatologist or skin care professional as soon as possible, as these may be signs of skin cancer.
How to Help Prevent Moles?
There is no guaranteed way to prevent moles, but there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing new moles or changes in existing moles:
- Protect your skin from the sun: Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and wide-brimmed hats, and use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30.
- Seek shade: Avoid being in direct sunlight for prolonged periods, especially between 10am and 4pm when the sun’s UV rays are strongest.
- Avoid tanning beds: Tanning beds emit UV rays that can increase the risk of developing moles and skin cancer.
- Check your skin regularly: Get into the habit of regularly checking your skin for any new or changing moles, and have any suspicious moles evaluated by a dermatologist or skin care professional.
- Be aware of your family history: If you have a family history of skin cancer, you may be at a higher risk of developing moles, so it’s important to take extra precautions to protect your skin.
By following these steps, you can reduce your risk of developing moles and increase the likelihood of early detection and treatment if needed.
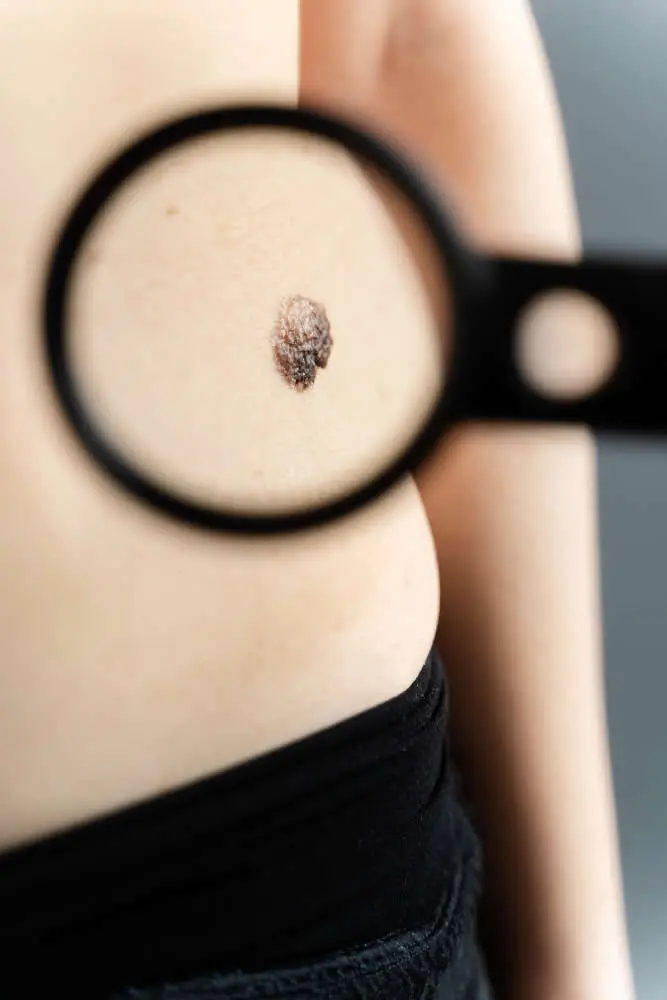
FAQ About Moles
Are moles harmful?
Most moles are benign, but in rare cases, moles can develop into skin cancer, so it’s important to monitor any changes in their appearance and have any suspicious moles evaluated by a dermatologist or skin care professional.
Can moles be removed?
Yes, moles can be surgically removed by a dermatologist or skin care professional, either by cutting them out, shaving them off, or using a laser.
Is it safe to remove a mole?
Removing a mole is generally safe, but it’s important to have the procedure performed by a qualified dermatologist or skin care professional to minimize the risk of complications.
How can I tell if a mole is cancerous?
Changes in a mole’s appearance, such as itching, bleeding, or changes in color, shape, or size, may be signs of skin cancer, and should be evaluated by a dermatologist or skin care professional as soon as possible.
Can moles return after removal?
In some cases, moles can return after removal, but this depends on various factors, such as the type, size, and location of the mole, as well as the method of removal.
Is there a dermatologist near me in St. Louis that offers treatment for moles?
Yes. At our St. Louis dermatology office we offer treatment for moles to patients from St. Louis and the surrounding area. Contact our office today to schedule an appointment.